Next | Prev | Up | Top | Contents | Index
Direct Memory Access
Some devices can perform direct memory access (DMA). In order to read or write a sequence of memory addresses, the device has to be told of the proper physical address range to use. This is done by storing target address numbers into device registers from the CPU. When the device's DMA address registers are loaded, it can access memory through the system bus, as shown in Figure 1-3.
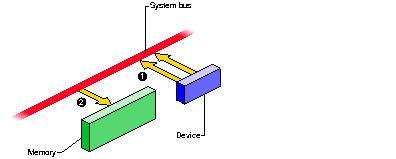
Figure 1-3 : Device Access to Memory
- The device places the next physical address, and data, on the system bus.
- The memory module stores the data.
When a device is programmed with an invalid physical address, the result is a bus error interrupt.
Next | Prev | Up | Top | Contents | Index

